

Heart failure can be classified into three groups: The term ejection fraction means the amount (percentage or fraction) of the blood in the biggest chamber of the heart (the left ventricle) that is pumped out (ejected) with each heartbeat before it fills up again for the next beat.It is normal for some of the blood to be left behind with each beat but usually at least half the blood is pumped out with every beat. Heart failure is also divided into types depending on how much blood the heart manages to pump out in each heartbeat. If you have chronic heart failure, it is possible to develop acute heart failure if matters suddenly become worse. As a general rule, you will often be admitted to hospital if you have acute heart failure, whereas if you have chronic heart failure you will probably have tests done as an outpatient.

If the symptoms have been going on for some time, it is called chronic heart failure. It is called acute heart failure if it has made you unwell quite suddenly. Heart failure is divided into types according to how suddenly it has come on.
#FLUID RETENTION CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE FULL#
If you have heart failure, your heart cannot cope with pumping the full amount of blood in each heartbeat. Ī ventricular assist device (bridge to transplant or as a destination therapy) or cardiac transplant is reserved for those with severe disease despite all other measures.In a normal healthy heart, during each heartbeat a set amount of blood enters the heart and is pumped out again. Most patients who satisfy the criteria for cardiac resynchronization therapy implantation are also candidates for an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and receive a combined device. Cardiac resynchronization therapy with biventricular pacing can improve symptoms and survival in selected patients who are in sinus rhythm and have a reduced left ventricular ejection fraction and a prolonged QRS duration. ĭevice therapy: Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is used for primary or secondary prevention of sudden cardiac death. In African-Americans, hydralazine plus oral nitrate is indicated in patients with persistent NYHA class III to IV HF and LVEF less than 40%, despite optimal medical therapy (beta-blocker, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, ARB, aldosterone antagonist (if indicated), and diuretics. Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors should not be given within 36 hrs of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors dose. Diuretic therapy is mainly used for symptom control. More limited evidence of survival benefit is available for diuretic therapy. Improved patient survival has been documented with the use of beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, hydralazine plus nitrate, and aldosterone antagonists. Combination therapy with these agents improves outcomes and reduces hospitalizations in patients with HF.
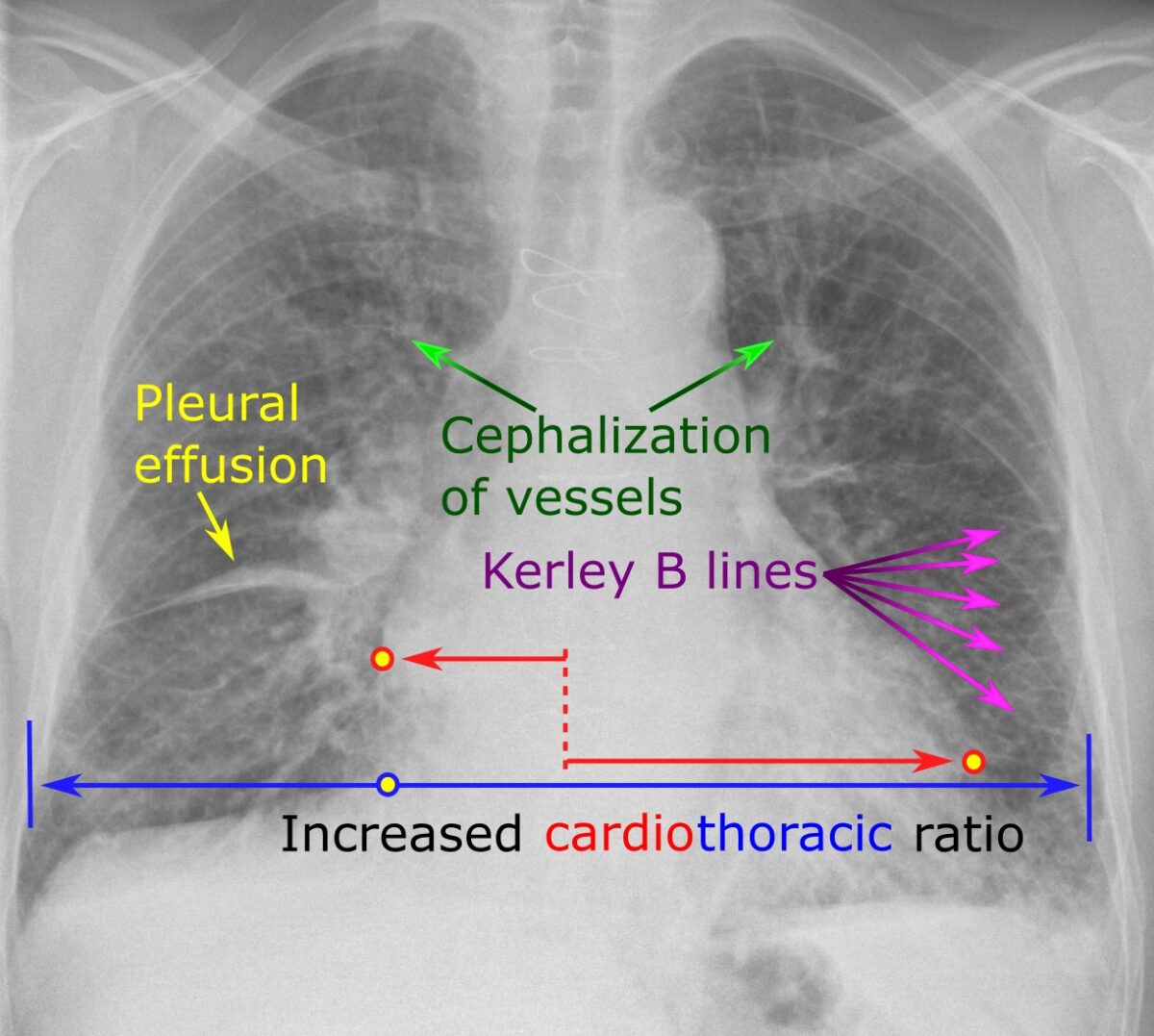
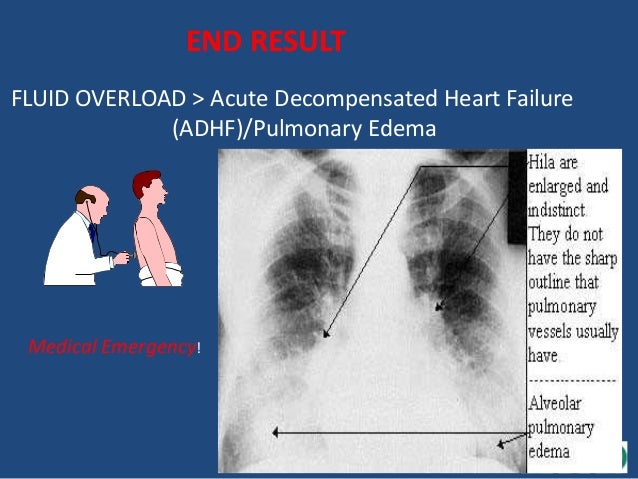
Diuretics, beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, hydralazine plus nitrate, digoxin, and aldosterone antagonists can produce an improvement in symptoms and are indicated for patients with HF based on their functional classification and severity of symptoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
